What is a Telecentric Imaging Lens? A Comprehensive Guide
A telecentric imaging lens is a special type of lens primarily used for high-precision imaging, such as in measurement systems, industrial inspection, and machine vision. Furthermore, with regular lenses, the image size changes as the object moves closer or farther away – this effect is called “perspective error”. However, in a telecentric lens, you will not encounter this problem because it is designed for constant magnification, regardless of whether the object is close or far from the focus point.
The central concept of the lens is that when the light rays enter the lens, they form a parallel image to the optical axis. Nevertheless, this means the lens only accepts rays that come in straight – this keeps the image size stable. A machine vision telecentric lens consists of three primary types:
1. Object-space Telecentric Lens – It is best for measurement accuracy
2. Image-space Telecentric Lens – It is suitable for stable image brightness
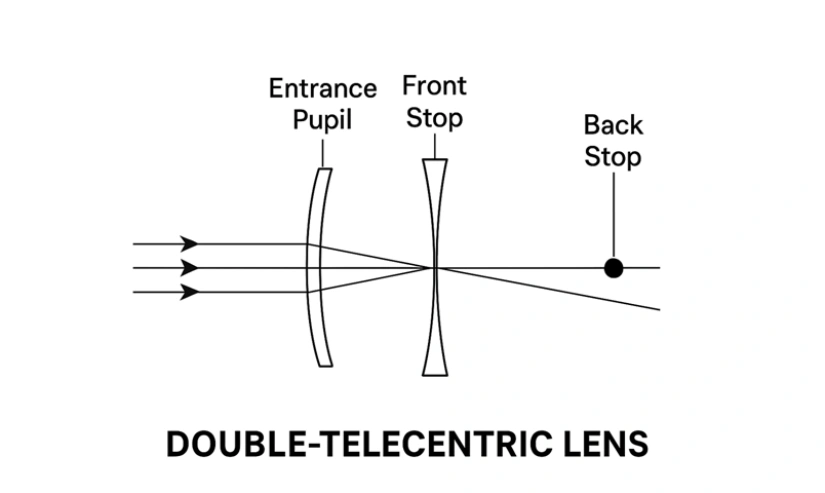
3. Double Telecentric – It has the qualities of object and image space telecentric lenses
Furthermore, it is mainly used for manufacturing inspection, microscopic imaging, and semiconductor testing. However, it is pretty expensive, but when it comes to precision and accuracy, it is the best choice.
Significant Principles of Telecentric Imaging Lens
A telecentric imaging lens is a system used to provide accurate image measurement, such as in a microchip manufacturing process. Furthermore, in this comprehensive system, you will find two telecentric lenses: one on the front and another on the back. Likewise, the front lens reflects light from the pupil to infinity, where the light rays form parallel rays inside the lens. The stop (or diaphragm) of this lens is placed at its back focal length position.
Additionally, a back lens is used, whose exit pupil lies at infinity, so that light rays emerge parallel to the image side as well. Moreover, the focal stop of this lens is at the front focal point. That means the stops of both lenses are at the same position, which is why it’s called double-telecentric lenses.
Nonetheless, this specific CCTV camera lens design is special because of its magnification (image size) function, which keeps the image steady even when the object shifts in or out. Hence, these lenses are used in applications where precision and measurement are significant, such as semiconductor lithography machines used to manufacture microchips.
Steps to Consider When Choosing the Right Telecentric Lens
Here are some key steps to consider when choosing the right machine vision telecentric lens for any industry.
1. Measure Sensor Dimensions
Formulas for calculation:
1. Sensor width = Total Number of horizontal pixels multiplied by accurate pixel size.
2. Height sensor height = Total number of vertical pixels multiplied by pixel size.
Example:
Sensor resolution: 5472 × 3648 pixels
Pixel size: 4.3 µm
Calculations:
Sensor width = 5472 × 4.3 µm = 23.53 mm
Sensor height = 3648 × 4.3 µm = 15.69 mm
Sensor diagonal = √(23.53² + 15.69²) ≈ 28.2 mm
2. Pick the required magnification
Magnification (m) = sensor total width / Preferred Field of View (F.O.V)
Example:
8.8 mm / 90 mm ≈ 0.098×
3. Choose the Minimum Required Optical Resolution
Minimum Resolution = 1 / (2 × entire pixel size)
For 2.8 µm pixels:
1 / (2 × 0.0028 mm) = 1 / 0.0056 mm ≈ 179 lp/mm
In lens, the Modulation Transfer Function should have at least MTF30 ≥ 179 lp/mm.
4. Determine the Telecentric Imaging Lens
Key pointers to keep in mind:
a. Field of View (F.O.V) at least 130mm
b. Resolution ≥ 145 line pairs per millimeter
c. Magnification around 0.11x
d. 17.5mm is appropriate for sensor diagonal
e. C mount telecentric lens is the best when mounted, illuminated, and used with the proper working distance
Working Functionality of Telecentric Imaging Lenses
| Parameter | Telecentric Imaging Lens Functionality |
|---|---|
| Chief Ray Direction | Parallel to the optical axis (object-space, image-space, or both) |
| Magnification Variation with Object Distance | ≈ 0% (constant magnification within telecentric range) |
| Perspective Error | Eliminated (no change in apparent object size with depth) |
| Field of View (FOV) | Fixed across object depth (constant within telecentric range) |
| Depth Sensitivity | Low — image size and shape remain constant for objects moving along the Z-axis |
| Working Distance Range | Limited (typically a few millimeters to centimeters, depending on lens design) |
| Aperture Stop Position | Placed at the front focal point of the optical system |
| Image Distortion | <0.1% (virtually negligible) |
| Numerical Aperture (NA) | Low to medium (reduces light collection but improves parallelism) |
| Depth of Field (DOF) | Narrow (requires stable object positioning) |
| Resolution Capability | High (suitable for precision measurement and metrology) |
| Illumination Requirement | High (due to low NA and reduced light throughput) |
| Common Configurations | Object-space telecentric, image-space telecentric, double telecentric |
| Typical Applications | Machine vision, metrology, dimensional inspection, microscopy |
| Optical Magnification Stability Range | Constant within ±0.1% across the telecentric region |
Images from a Telecentric Lens
When a standard or conventional machine vision telecentric lens forms an image, the magnification depends on the object’s distance. However, this means that if an object is close to the lens, the image will appear larger, and if it is farther away, the image will appear smaller. Therefore, when a machine vision system measures the size of something, such as the width of PCB tracks, it does so. Likewise, if the PCB is slightly forward or backward, the measurement may be inaccurate because the magnification changes.
A telecentric CCTV camera lens solves this problem. Furthermore, the magnification of this lens remains constant regardless of the object’s distance. Nevertheless, this means that the image formed by a telecentric lens has no size distortion. This type of image is called an orthographic image. An orthographic view is a 2D (two-dimensional) representation that shows only length and width, not the object’s actual depth.
For example, a cylinder appears to be a rectangle when viewed from the side, whereas viewed from the top, it appears to be a circle. However, this view is formed by parallel lines that are perpendicular to the object.
Image: Orthographic Views of a Cylinder
(Side View → Rectangle, Top View → Circle)
This precise type of view does not provide an accurate depth of the object. Thus, it only gives you an idea of different shapes and sizes.
The C mount telecentric lens is accurate and compact. In a telecentric lens, the main light rays are parallel to the optical axis, meaning the lens accepts only light rays that are perpendicular to it. Therefore, its field of view is very narrow.
Its interesting effect is that, when two objects are placed next to each other, they appear side by side in a telecentric lens. It means that there will be no difference in depth in the image. Nevertheless, this property ensures measurements are consistent and accurate, even when the objects are slightly offset
Advantages and Disadvantages of Telecentric Imaging Lens
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Constant Magnification | Expensive |
| No Perspective Error | Limited Field of View |
| High Measurement Accuracy | Larger Size and Weight |
| Consistent Image Quality | Limited Working Distance Range |
| Depth-Independent Inspection | Lower Light Efficiency |
It’s Time to Wrap Things Up!
We understand the importance of invaluable tools for precise, stable imaging, offering unmatched applications for measuring comprehensive features, profiles, and objects at indefinite or variable distances. Moreover, several engineers and researchers find the telecentric imaging lens filled with exceptional advantages, which help them get high accuracy, reliability, and efficiency across different industries.
However, if you are searching for a perfect solution for different kinds of cameras, lenses, or camera parts for various purposes, look no further than Superior CCTV. The expert at Superior CCTV will assist you when choosing the right lens. Furthermore, you need to submit your precise requirements and have a word with our experts. So, it’s time to improve your security monitoring with Superior CCTV today!

